Dip Coating Application Technology

Introduction to Dip Coating
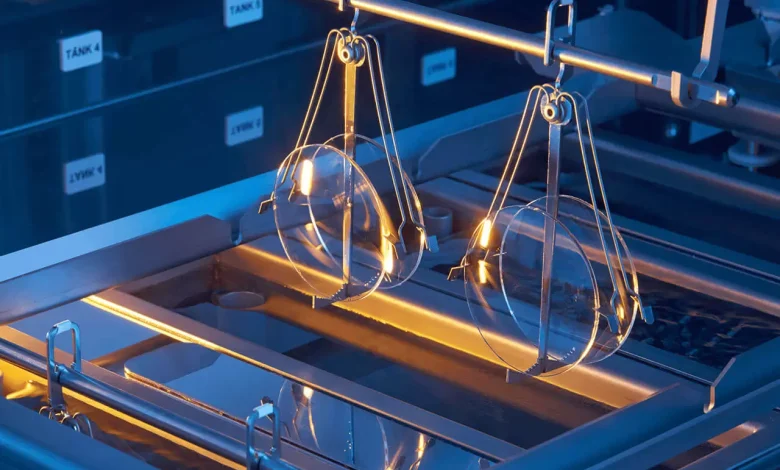
Dip coating is a widely used technique in industrial applications to apply thin, Dip coating application technology uniform layers of coating material onto a surface. This method involves immersing a substrate into a liquid coating material and then withdrawing it at a controlled speed, allowing the coating to adhere to the surface evenly. The technology is commonly employed in sectors like automotive, electronics, and medical devices, where high precision and efficiency are crucial.
Dip coating is favored for its ability to consistently apply coatings to a wide variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, plastics, and glass. The process can be used to impart properties like corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, electrical insulation, and aesthetic appeal. The technology behind dip coating has evolved to offer high degrees of control over the coating thickness, uniformity, and surface quality, making it suitable for a wide array of both industrial and research-based applications.
The Dip Coating Process
The dip coating process typically involves four key stages: immersion, dwell time, withdrawal, and drying or curing. Each stage plays a crucial role in determining the final quality and characteristics of the coating.
1. Immersion Stage
The first stage of the dip coating process is immersion. During this step, industrial dip coating machine the substrate is completely submerged into the liquid coating solution. The time and depth of immersion are carefully controlled based on the desired thickness of the coating.
The immersion depth and time are meticulously controlled based on the thickness and properties desired in the final coating. For example, a deeper immersion can result in a thicker coating. Proper control during this phase is critical because it lays the foundation for uniform coverage.
2. Dwell Time
Once the substrate is fully immersed in the coating solution, it remains in the liquid for a predetermined amount of time—this is known as the dwell time. The duration of this phase is critical as it allows the coating material to uniformly wet and penetrate the surface of the substrate. During this time, the viscosity of the solution and the surface properties of the substrate significantly influence the coating behavior.
For instance, highly viscous solutions will require longer dwell times to ensure complete wetting, while substrates with hydrophobic surfaces might need special preparation to allow even coating adhesion. The goal of this step is to achieve a uniform layer across the entire surface of the substrate.
3. Withdrawal
The withdrawal stage is one of the most crucial steps in the dip coating process. It determines both the thickness and uniformity of the final coating. During this phase, the substrate is carefully and steadily pulled out of the coating solution at a controlled speed. The speed at which this withdrawal occurs directly influences the thickness of the coating layer: slower withdrawal speeds typically result in thicker coatings due to the accumulation of more material, while faster speeds produce thinner layers.
Precision in controlling the withdrawal rate is vital for achieving the desired coating thickness, especially in applications where minute variations can affect the performance of the final product. For example, in the electronics industry, even slight inconsistencies in the thickness of insulating coatings could lead to performance issues or device failure.
4. Drying and Curing
After the substrate has been withdrawn from the coating solution, it undergoes a drying or curing process to solidify and fix the coating material onto the surface. This phase can involve various methods depending on the type of coating material being used. Common drying techniques include air drying, where the coated substrate is exposed to ambient conditions, or forced drying using heat. In cases where UV-curable materials are used, the substrate is exposed to ultraviolet light to initiate a photochemical reaction that hardens the coating.
The drying or curing process must be carefully managed to avoid defects such as bubbles, cracks, or uneven surfaces. Properly executed, this step ensures a durable, smooth, and adherent coating, ready for the intended application.
Benefits of Dip Coating
Dip coating offers several advantages, making it a preferred coating method for many industrial applications. Some of its key benefits include:
1. Precision and Uniformity
One of the major advantages of dip coating technology is its ability to create uniform layers with high precision. This is particularly important in industries where consistent surface coatings are required to ensure product performance.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Dip coating is a cost-effective technique for applying surface treatments. Since excess coating material typically drips back into the solution during the withdrawal stage, material waste is minimized, leading to significant cost savings. Furthermore, the simplicity of the process means that less labor and lower maintenance costs are required compared to more complex coating methods, such as spray coating or electroplating.
3. Versatility in Materials and Applications
Another significant benefit of dip coating is its versatility. The technology can be applied to a wide range of substrate materials, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and glass. It is also capable of handling various coating types, from simple paints and varnishes to advanced polymer solutions and nanoparticle suspensions. This adaptability makes dip coating suitable for numerous industrial applications, from protective coatings for automotive parts to bioactive coatings for medical implants.
Industrial Applications of Dip Coating
The versatility and precision of dip coating make it suitable for use in various industries. Some key applications include:
1. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, dip coating is frequently used to apply protective coatings to vehicle components. These coatings enhance the durability and resistance of parts to corrosion, wear, and environmental factors. Dip coating is particularly beneficial for automotive parts with complex shapes, such as chassis components or engine parts, where uniform coverage can be difficult to achieve with other coating methods.
2. Electronics
The electronics industry relies heavily on dip coating for the application of protective coatings to sensitive components. Thin insulating or moisture-resistant layers are often applied to delicate parts such as printed circuit boards (PCBs) or sensors. The precision of dip coating ensures that these protective layers are applied evenly without compromising the functionality of the components.
3. Medical Devices
In the medical field, dip coating is used to apply specialized coatings to devices such as catheters, stents, and implants. These coatings may be designed to enhance biocompatibility, prevent infection, or provide drug-eluting properties. The ability to create uniform, reliable coatings is critical in this industry, where the performance of a device can directly impact patient health.
4. Optical and Glass Coatings
Dip coating is also widely used in the production of optical devices and glassware. Anti-reflective coatings, for example, can be applied to lenses, mirrors, and display screens using the dip coating process. This technique ensures that the coatings are even and free of defects, which is essential for maintaining the optical clarity and performance of these products.
Conclusion
Dip coating is a versatile, cost-effective, and precise method for applying coatings across a wide range of industries. Its ability to create uniform coatings on complex surfaces makes it a valuable tool for industries that demand high-quality surface treatments, from automotive and electronics to medical devices and optics. The simplicity of the process, coupled with its adaptability to different materials and coatings, ensures that dip coating will continue to be a popular choice for manufacturers seeking reliable, efficient coating solutions